
An exteroceptor is a receptor that is located near a stimulus in the external environment, such as the somatosensory receptors that are located in the skin. These cells release neurotransmitters onto a bipolar cell, which then synapses with the optic nerve neurons.Īnother way that receptors can be classified is based on their location relative to the stimuli. Photoreceptors in the eyes, such as rod cells, are examples of (c) specialized receptor cells.
#SOMATIC SENSORY NEURON DENDRITE LOCATION FREE#
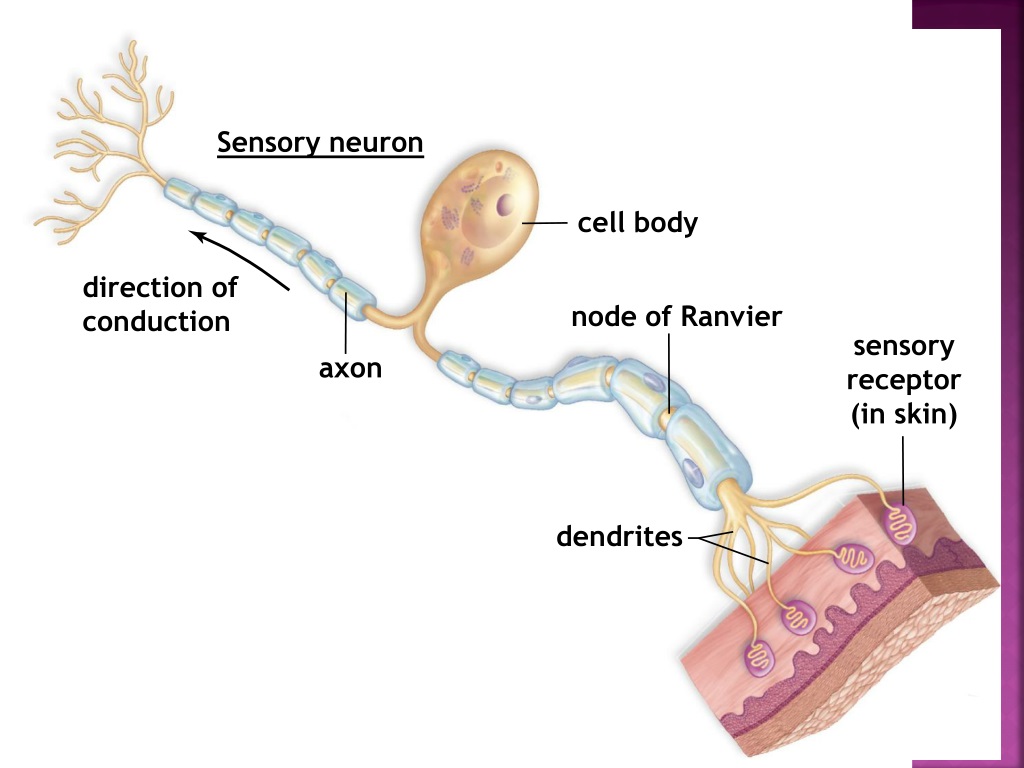
Sensory neurons can have either (a) free nerve endings or (b) encapsulated endings.
The cells in the retina that respond to light stimuli are an example of a specialized receptor, a photoreceptor.įigure 14.2 Receptor Classification by Cell Type Receptor cell types can be classified on the basis of their structure.
#SOMATIC SENSORY NEURON DENDRITE LOCATION SKIN#
Also located in the dermis of the skin are lamellated corpuscles, neurons with encapsulated nerve endings that respond to pressure and touch. The pain and temperature receptors in the dermis of the skin are examples of neurons that have free nerve endings. The cells that interpret information about the environment can be either (1) a neuron that has a free nerve ending, with dendrites embedded in tissue that would receive a sensation (2) a neuron that has an encapsulated ending in which the sensory nerve endings are encapsulated in connective tissue that enhances their sensitivity or (3) a specialized receptor cell, which has distinct structural components that interpret a specific type of stimulus ( Figure 14.2). They can also be classified functionally on the basis of the transduction of stimuli, or how the mechanical stimulus, light, or chemical changed the cell membrane potential. Receptors can be classified structurally on the basis of cell type and their position in relation to stimuli they sense. Receptor cells can be classified into types on the basis of three different criteria: cell type, position, and function. Different types of stimuli are sensed by different types of receptor cells. Stimuli in the environment activate specialized receptor cells in the peripheral nervous system. Physical changes in these proteins increase ion flow across the membrane, and can generate an action potential or a graded potential in the sensory neurons. Other transmembrane proteins, which are not accurately called receptors, are sensitive to mechanical or thermal changes. For example, a molecule in food can serve as a ligand for taste receptors. Transmembrane receptors are activated by chemicals called ligands. A transmembrane protein receptor is a protein in the cell membrane that mediates a physiological change in a neuron, most often through the opening of ion channels or changes in the cell signaling processes. A receptor cell is changed directly by a stimulus. Receptors are the cells or structures that detect sensations. Perception is dependent on sensation, but not all sensations are perceived. Perception is the central processing of sensory stimuli into a meaningful pattern. Sensation is the activation of sensory receptor cells at the level of the stimulus.

The central integration may then lead to a motor response.ĭescribing sensory function with the term sensation or perception is a deliberate distinction. The stimulus causes the sensory cell to produce an action potential that is relayed into the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated with other sensory information-or sometimes higher cognitive functions-to become a conscious perception of that stimulus. This occurs when a stimulus changes the cell membrane potential of a sensory neuron. Stimuli from varying sources, and of different types, are received and changed into the electrochemical signals of the nervous system.

Describe the structures responsible for the special senses of taste, smell, hearing, balance, and vision.Describe different types of sensory receptors.By the end of this section, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
